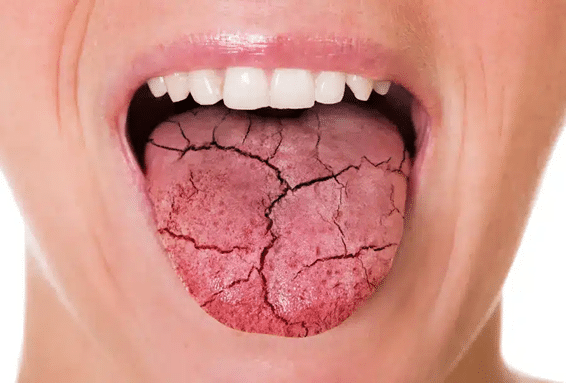
Why does diabetes and dry mouth happen?
In this blog we can help you understand the link between diabetes and dry mouth. Create an understanding of why diabetes can cause dry mouth, can reduce dry mouth issues. Starting with high blood sugar levels can lead to frequent urination and dehydration, which can then result in a dry mouth. Additionally, diabetes can affect the salivary glands and reduce saliva production, also leading to dry mouth symptoms.
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can have various effects on the body. One common symptom experienced by individuals with diabetes is dry mouth, also known as xerostomia. Dry mouth occurs when there is a lack of saliva production in the mouth, leading to oral discomfort and potential dental problems. Understanding the link between diabetes and dry mouth is essential for diabetic patients to effectively manage their oral health. In this blog, we will explore the prevalence of dry mouth in diabetics, the factors contributing to dry mouth, the effects of hyperglycemia on oral health, salivary gland dysfunction, the impact of diabetes medications, the role of insulin, the importance of glycemic control, the complications of dry mouth, and practical tips for preventing dry mouth from diabetes. Let’s delve deeper into the connection between diabetes and dry mouth and the implications it has on oral health.
The Prevalence of Dry Mouth from Diabetes
Dry mouth is a prevalent issue among individuals with diabetes, affecting a significant percentage of the diabetic population. Research suggests that the prevalence of xerostomia from diabetes ranges from 30% to 70%. This high prevalence emphasizes the importance of understanding and addressing the association between diabetes and dry mouth symptoms. By recognizing the prevalence of dry mouth in diabetics, healthcare professionals can provide tailored advice and interventions to manage this common oral health concern.
Importance of Understanding Diabetes and Oral Health
Understanding the relationship between diabetes and oral health is crucial for diabetic patients. Diabetes mellitus, the most common form of diabetes, can have profound effects on the health of the mouth and teeth. Oral health is an essential aspect of diabetes management as diabetes patients are more prone to common oral health problems, including dry mouth, gum disease, tooth decay, and oral infections. By prioritizing oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and maintaining blood glucose levels within a healthy range, diabetic patients can prevent long-term oral complications and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding Xerostomia from Diabetes
Xerostomia (zeer-uh–stoh-mee-uh), or dry mouth, is a prevalent condition experienced by individuals with diabetes. Xerostomia from diabetes occurs due to reduced saliva flow in the mouth, leading to oral dryness and potential oral health problems. Understanding xerostomia from diabetes is crucial to address the symptoms and implications of dry mouth effectively. By exploring the factors contributing to dry mouth in diabetics, common symptoms, underlying causes, and potential complications, diabetic patients can take proactive measures to manage xerostomia and maintain good oral health.
Factors Contributing to Diabetes and Dry Mouth
Several factors contribute to dry mouth in individuals with diabetes. Firstly, high blood sugar levels can affect the salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva production. Lack of saliva in the mouth can result in dryness and discomfort. Diabetes-related medications, including certain oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin, may also cause dry mouth as a side effect. Dehydration, common in diabetes, can exacerbate dry mouth symptoms. Additionally, underlying health conditions, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and endocrine disorders, can contribute to dry mouth in diabetics.
Common Symptoms of Xerostomia
Xerostomia from diabetes is characterized by various symptoms. Common symptoms of dry mouth in diabetics include oral dryness, a sticky feeling in the mouth, and the need for frequent sips of water. Dry mouth can cause bad breath, cracked lips, mouth sores, and difficulty swallowing. Dry mouth symptoms can also lead to dental problems, such as tooth decay, gum disease, and sensitive teeth. Recognizing the symptoms of dry mouth from diabetes is crucial in seeking appropriate management strategies and professional advice to effectively alleviate the discomfort and prevent oral health complications associated with xerostomia.
What is Xerostomia
Xerostomia, commonly referred to as dry mouth, is a condition characterized by a lack of moisture in the mouth. With xerostomia, the salivary glands do not produce enough saliva, leading to oral dryness and potential oral health problems. Dry mouth can cause discomfort, difficulty speaking and swallowing, and an increased risk of dental issues. Xerostomia from diabetes may result from underlying health conditions, high blood sugar levels, certain medications, or nerve damage. Managing xerostomia involves addressing the underlying causes, relieving dry mouth symptoms, and implementing good oral hygiene practices to maintain overall oral health.
Hyperglycemia and Its Effects on Oral Health
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels, in diabetes is closely linked to the prevalence of dry mouth due to several interconnected factors:
- Reduced Saliva Production:
- Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to dehydration as the body attempts to eliminate excess glucose through increased urine output.
- Dehydration, in turn, reduces the production of saliva, contributing to the dry mouth sensation.
- Neuropathy:
- Chronic high blood sugar levels can cause damage to nerves throughout the body, a condition known as neuropathy.
- The salivary glands are not immune to the effects of neuropathy, and damage to the nerves controlling saliva production can result in decreased saliva flow, exacerbating dry mouth symptoms.
- Compromised Immune Function:
- Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, including those affecting the oral cavity.
- Infections in the mouth can lead to inflammation and further compromise the function of salivary glands, exacerbating dry mouth.
- Medication Side Effects:
- Some medications commonly used to manage diabetes may have dry mouth as a side effect.
- These medications can either directly affect saliva production or contribute to dehydration, intensifying the dry mouth condition.
- Altered Microbial Balance:
- Elevated glucose levels in saliva provide an environment conducive to the growth of harmful bacteria.
- The imbalance in oral microbial flora can contribute to conditions such as gum disease and infections, further aggravating dry mouth.
- Impaired Wound Healing:
- Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds, including those in the oral cavity.
- Dry mouth can lead to oral sores, and the compromised wound healing capacity in diabetics can prolong the discomfort associated with these sores.
Addressing hyperglycemia is crucial not only for managing diabetes but also for alleviating dry mouth symptoms. Maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range through proper diabetes management can help mitigate the impact on saliva production and reduce the risk of associated complications. Additionally, using products like Lubricity dry mouth spray can offer targeted relief by providing long-lasting moisture and supporting overall oral health for individuals managing diabetes and experiencing dry mouth.
Managing Diabetes and Dry Mouth with Common Medications
Various medications used to manage diabetes can have side effects, affecting both overall health and contributing to symptoms like dry mouth. It’s important to note that the specific side effects can vary depending on the type of medication, individual responses, and other health factors. Here is a general list of potential side effects associated with common diabetes medications, along with a focus on the occurrence of dry mouth:
- Metformin (Biguanide):
- Common side effects: Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort).
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect of metformin.
- Sulfonylureas (e.g., Glipizide, Glimepiride):
- Common side effects: Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain.
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect but can occur due to changes in blood sugar levels.
- Meglitinides (e.g., Repaglinide, Nateglinide):
- Common side effects: Hypoglycemia, weight gain.
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect but may be indirectly related to changes in blood sugar levels.
- Thiazolidinediones (e.g., Pioglitazone, Rosiglitazone):
- Common side effects: Fluid retention, weight gain, increased risk of fractures.
- Dry mouth is not a common side effect but can occur due to associated fluid retention.
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors (e.g., Sitagliptin, Saxagliptin):
- Common side effects: Upper respiratory tract infections, headaches.
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect, but individuals may experience changes in taste.
- Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors (e.g., Canagliflozin, Empagliflozin):
- Common side effects: Genital yeast infections, urinary tract infections, increased urination.
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect but can occur due to increased urination.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists (e.g., Exenatide, Liraglutide):
- Common side effects: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Dry mouth is not a typical side effect but may occur due to gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Insulin:
- Common side effects: Hypoglycemia, weight gain.
- Dry mouth is not a direct side effect of insulin, but low blood sugar levels can cause symptoms such as thirst and dry mouth.
It’s crucial for individuals with diabetes to discuss potential side effects with their healthcare providers.
Managing Diabetes Dry Mouth Symptoms While on Medication
Managing dry mouth symptoms from diabetes requires active steps to alleviate discomfort and support oral health. While taking diabetes medications, diabetic patients can take several measures to manage dry mouth symptoms. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help combat oral dryness. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy can stimulate saliva production. Using a humidifier in the bedroom can help keep the mouth moist, especially during sleep. Practicing good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent dental problems associated with dry mouth from diabetes. Additionally, using saliva substitutes or oral rinses recommended by healthcare professionals can provide relief from dry mouth symptoms.
What Do Dentists Recommend for Managing Diabetes and Dry Mouth?
Dentists play a vital role in managing dry mouth symptoms from diabetes. They can provide tailored advice and recommendations for dry mouth management. Dentists often recommend staying hydrated by drinking water throughout the day. Lubricity Dry Mouth Spray is also recommended because it is a great saliva substitute created for relieving dry mouth symptoms.
Why Do Dentists Recommend Lubricity for Dry Mouth?
The inclusion of hyaluronic acid is crucial in Lubricity, as it not only acts as a highly effective moisturizing agent, ensuring sustained oral hydration, but also contributes to tissue healing and comfort, making it an essential component for comprehensive dry mouth relief. Lubricity is sugar free, alcohol free and gluten free. This makes Lubricity a great choice for diabetics because there are zero calories and no ingredient in it that would spike blood sugar. Lubricity is a saliva substitute that begins working immediately and provides up to 4 hours of dry mouth relief when used as directed. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy can stimulate saliva production. However, with Lubricity you get the added benefit of Xylitol which promotes good oral health. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is essential for preventing dental problems associated with dry mouth. Regular dental check-ups, typically every six months, allow dentists to monitor oral health, address dry mouth concerns, and provide necessary treatments or interventions to manage dry mouth from diabetes effectively.
The Importance of Glycemic Control
Glycemic control, or maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range, is of utmost importance when it comes to diabetes management. Effective glycemic control is crucial in preventing the complications associated with diabetes, including oral health problems such as dry mouth. Diabetes patients who achieve optimal blood sugar levels through medication, dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and proper diabetes management strategies can significantly reduce the risk of dry mouth symptoms and oral health complications. Recognizing the importance of glycemic control in diabetes empowers diabetic patients to prioritize blood sugar management, supporting overall oral health and general well-being.
Glycemic Control and Xerostomia – What’s the Link?
The link between glycemic control and xerostomia, or dry mouth, highlights the importance of proper blood sugar management in diabetics. Poor glycemic control, characterized by high blood sugar levels, can contribute to the prevalence of dry mouth symptoms from diabetes. By achieving optimal blood sugar levels through glycemic control, diabetes patients can minimize the risk of xerostomia and oral health problems associated with dry mouth. Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, following healthcare provider recommendations, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments can support glycemic control efforts and help manage dry mouth diabetes effectively.
Tips for Maintaining Good Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining good blood sugar levels is crucial in diabetes management, supporting overall health and oral health. Diabetic patients can follow these tips to help maintain optimal blood sugar levels:
- Adhere to the diabetes management plan recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Follow a balanced diet, consisting of whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables, while limiting sugary foods and drinks.
- Engage in regular physical activity and exercise, as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, using a blood glucose meter or other monitoring devices.
- Take diabetes medications, including insulin, as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
By implementing these tips, diabetic patients can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, improving glycemic control and, consequently, supporting oral health in diabetes.
Insulin and its Impact on Oral Health
Insulin plays a crucial role in diabetes management, but what impact does it have on oral health? Insulin is essential for controlling blood glucose levels in diabetes, ensuring the body can effectively utilize glucose for energy. By maintaining optimal blood glucose levels, insulin indirectly supports oral health in diabetics. Healthy blood glucose levels help prevent oral health problems, including dry mouth, gum disease, tooth decay, and oral infections.
Understanding the Role of Insulin in Diabetes Management
Insulin plays a vital role in diabetes management, impacting blood glucose levels and overall health. For individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or does not effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin therapy is commonly used to control blood glucose levels and support diabetes management. By administering insulin, diabetic patients can regulate their blood glucose levels, preventing high blood sugar levels that can contribute to oral health problems.
Can Insulin Cause Dry Mouth?
While dry mouth is not a common side effect of insulin therapy, diabetic patients may still have concerns about the potential impact of insulin on oral health. It is important to note dry mouth symptoms from diabetes are not typically attributed to insulin use. Even though dry mouth is one of the less common side effects, your overall health is a major concern which can result in kidney, heart, and foot damage as a diabetic management issue that you should be keeping an eye on.
Complications of Diabetics and Dry Mouth
Untreated dry mouth from diabetes can have potential complications and impact on oral health. The lack of saliva in the mouth creates an environment that promotes the growth of bacteria, increasing the risk of dental caries, or tooth decay. Dry mouth from diabetes can also contribute to gum disease, characterized by inflammation, bleeding gums, and potential tooth loss. Additionally, untreated dry mouth can lead to bad breath, oral infections, oral sores, sensitive teeth, and difficulty in speaking and swallowing.
The Importance of Early Intervention and Oral Care
Early intervention and oral care play essential roles in managing dry mouth symptoms from diabetes. By addressing dry mouth symptoms early, diabetic patients can prevent the development of oral health complications, such as tooth decay, gum disease, and oral infections. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are vital in monitoring oral health, identifying potential problems, and implementing appropriate interventions. Good oral care practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and the use of mouth rinses, support oral hygiene in diabetes patients.
Why Shop for Lubricity Dry Mouth Oral Spray?
Lubricity Dry Mouth Oral Spray offers a targeted solution to alleviate the symptoms and complications associated with dry mouth in individuals with diabetes. Its advanced formula not only provides long-lasting moisture to relieve dryness but also addresses specific oral health challenges faced by diabetics. By maintaining proper oral hydration, Lubricity helps reduce the risk of dental issues, fostering a healthier oral environment.
As an added benefit, we are pleased to offer a 20% discount on Lubricity Dry Mouth Oral Spray to see how well our product works for you. Simply use the code “DRY20” at checkout to enjoy the advantages of Lubricity at an exclusive discounted rate. This special offer aims to make effective dry mouth relief more accessible for individuals with diabetes, ensuring that they can experience the benefits of Lubricity’s targeted solution at an affordable price. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to enhance your oral health and well-being with Lubricity.
How to Prevent Diabetes and Dry Mouth
Preventing dry mouth from diabetes is crucial for maintaining good oral health and overall well-being. Diabetic patients can take proactive measures to prevent dry mouth symptoms by implementing the following strategies:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing.
- Avoid foods high in salt, as they can contribute to oral dryness.
- Limit the consumption of alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, as they can exacerbate dry mouth symptoms.
- Consider using saliva substitutes, oral rinses, or moisturizers recommended by healthcare professionals.
- By adopting these strategies and prioritizing oral health, diabetic patients can effectively prevent dry mouth symptoms, reduce the risk of oral health complications, and enhance their overall quality of life.
Practical Tips and Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Dry Mouth
Preventing dry mouth from diabetes involves implementing practical tips and lifestyle changes to promote oral health and moisture in the mouth. Diabetic patients can try the following:
- Stay hydrated by drinking water throughout the day.
- Chew sugar-free gum or suck on sugar-free candy to stimulate saliva production.
- Use a humidifier in the bedroom to add moisture to the air.
- Limit the consumption of salty and sugary foods, alcohol, and caffeine.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, as stress can contribute to dry mouth symptoms.
- By incorporating these lifestyle changes into their daily routine, diabetic patients can support saliva production, prevent dry mouth symptoms, and maintain good oral health.
How Regular Dental Check-ups Can Help Manage Dry Mouth?
Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in managing dry mouth symptoms from diabetes. During dental visits, dentists can assess the oral health of diabetic patients, specifically addressing concerns related to dry mouth. Dentists may recommend appropriate treatments, oral hygiene practices, and interventions to manage dry mouth effectively. Dental cleanings can help prevent gum disease, tooth decay, and other oral health problems associated with dry mouth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to understand the link between diabetes and dry mouth. Dry mouth, or xerostomia, is a common symptom among diabetics and can have significant implications for oral health. Elevated blood sugar levels, medications, and salivary gland dysfunction all contribute to the development of dry mouth in diabetics. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to manage their blood sugar levels effectively and practice good oral hygiene to prevent complications associated with dry mouth. Regular dental check-ups and lifestyle changes, such as staying hydrated and avoiding certain medications, can also help prevent and manage dry mouth symptoms. Remember to share this valuable information on social media to raise awareness about the connection between diabetes and dry mouth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, dry mouth is a common symptom of diabetes. Dry mouth occurs when there is a reduced production of saliva in the mouth, leading to oral dryness and potential oral health problems. Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves that control salivary glands, resulting in dry mouth symptoms. If you have diabetes and experience dry mouth, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to explore potential causes, effective management strategies, and preventive measures. By addressing dry mouth symptoms, diabetic patients can alleviate oral discomfort, support oral health, and enhance their overall well-being.
People with diabetes are more likely to experience dry mouth due to various factors, including the impact of diabetes on the salivary glands and the potential underlying causes of dry mouth. Diabetes can cause damage to the nerves that control the salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva production and dry mouth symptoms. Additionally, high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can contribute to salivary gland dysfunction, affecting the flow of saliva and resulting in dry mouth. The combination of these factors makes individuals with diabetes more susceptible to dry mouth, necessitating proper oral care and management of the underlying causes of dry mouth from diabetes.
Dry mouth can have significant effects on a person’s overall health and well-being. Oral dryness can cause discomfort while speaking, eating, and swallowing, potentially impacting a person’s ability to communicate, consume food, and maintain proper nutrition. Dry mouth can result in bad breath, sensitive teeth, oral sores, and an increased risk of dental problems such as tooth decay and gum disease. Chronic dry mouth can also affect a person’s ability to sleep, leading to fatigue and a decrease in overall energy levels. Maintaining good oral health, including managing dry mouth symptoms, is crucial in supporting overall health and well-being in individuals, particularly those with diabetes.
The symptoms of dry mouth in diabetics may include:
- Reduced Saliva Production
- Persistent Thirst
- Difficulty Swallowing or Speaking
- Sore Throat
- Burning Sensation
- Altered Taste
- Difficulty Wearing Dentures
- Increased Dental Issues
- Bad Breath